Musculoskeletal pain affects the bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, or muscles. A fracture, for example, can result in severe pain. A chronic condition like arthritis can also be the cause of pain. Speak with a doctor if musculoskeletal pain interferes with your normal activities. Effective treatments can alleviate pain.
Musculoskeletal pain can be acute, which means it occurs suddenly and severely. Alternatively, the pain may be chronic (long-lasting). You may experience pain-associated pain (pain in one area of your body) or discomfort throughout your entire body.
4 Types of musculoskeletal pain:
Bone pain:
Bone pain is caused by injuries such as bone fractures or other musculoskeletal pain. A tumor may occasionally cause bone pain.
Joint pain:
Stiffness and inflammation frequently come before joint pain. Many patients find that joint discomfort improves with rest and increases with activity.
Muscle pain:
Muscle spasms, cramps, or injuries can all cause muscle pain. Infections or tumors can also cause muscle discomfort.
Ligament and tendon pain:
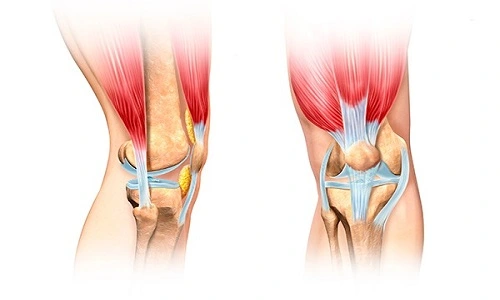
Ligaments and tendons are tough bands of tissue that link your bones and joints. Tendon and ligament discomfort can result from sprains, strains, and overuse injuries.
Causes of musculoskeletal pain:
- Fractures in the bones
- Dislocation of a joint (when something forces a joint out of its proper position)
- Blows to the muscles, bones, or joints
- Injuries caused by overuse
- Bad posture
- Sprains
Symptoms of musculoskeletal pain:
- Stiffness and aching
- Muscle pain and burning
- Fatigue
- A muscle twitch occurs
- Movement causes pain that worsens
- Disruptions in sleep
- Diagnosis
Before beginning a diagnostic, your doctor looks over your medical history.
Your doctor may ask you questions to determine:
- If you have any further symptoms, such as a rash or fever,
- Regardless of whether your pain is acute or chronic,
Which factors worsen or alleviate pain?
Finally, your doctor performs a hands-on diagnosis to find the source of the pain. The affected region may be treated.
What is the treatment for musculoskeletal pain?
Types of treatments include:
- Acupuncture
- Chiropractic manipulation
- Occupational therapy
- Analgesics are pain relievers
- Therapy for the body
- Splints
- Injections of steroids
- Massage can be therapeutic
Is it possible to manage musculoskeletal discomfort at home?
Your doctor may guide you on how to manage musculoskeletal pain at home.
Suggestions may include the following:
- The use of hot and cold therapy
- Pain remedies sold over the counter
- Exercising for strength and conditioning
- Exercising your legs
- Techniques for reducing stress
What medications are used to treat musculoskeletal pain?
Carisoprodol brand name “Pain o soma” is an FDA-approved Skeletal Muscle Relaxants medicine. It is used to relieve the discomfort associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal pain.
How does Pain o soma (Carisoprodol) treat Musculoskeletal Pain?
Soma is a muscle relaxant that works by blocking pain signals between the nerves and the brain. Mostly prescribed Pain o Soma 500mg and Pain o Soma 350mg are used to treat musculoskeletal pain or injury in associated with rest and physical therapy.
Carisoprodol’s sedative effects, which contribute to its medicinal and recreational usage, are largely linked to the actions of meprobamate, its major metabolite, at GABAA receptors (GABAAR).
What can I do to avoid musculoskeletal pain?
It is critical to maintain strong bones and joints to prevent musculoskeletal pain.
You can avoid musculoskeletal pain by doing the following:
- Repetitive movements should be avoided
- Maintain proper posture
- Lifting skills should be practiced
- Stretch regularly
Risk for musculoskeletal pain
Certain conditions can raise your risk of musculoskeletal pain, such as:
Persistent joint inflammation is the root cause of arthritis.
Joint pain and stiffness are common symptoms of arthritis.
Fibromyalgia is a chronic disorder that causes widespread musculoskeletal pain and fatigue. Fibromyalgia patients frequently complain of muscular, tendon, or ligament discomfort.
Nerve compression or pinched nerves are caused by some disorders known as “tunnel” syndromes. Carpal tunnel syndrome, cubital tunnel syndrome, and tarsal tunnel syndrome are a few instances of these diseases. Overuse injuries are frequently the root cause of these disorders.
How should you deal with musculoskeletal pain?
To manage musculoskeletal pain, try the following:
- Avoid smoking, which contributes to inflammation.
- Consume a healthy, anti-inflammatory diet.
- Rest the muscle, joint, or bone that has been injured.
- Stretch at least once a day, or as often as your healthcare provider recommends.
- Using Soma 500 mg Tablet Pain Reliever is the most effective way
- To reduce swelling and inflammation, apply cold and heat.
FAQS:
What does it feel like to have musculoskeletal pain?
Some patients with moderate musculoskeletal pain report the sensation as being akin to an overworked or strained muscle. A frequent symptom is regional discomfort in a single joint. Musculoskeletal pain patients frequently experience body pains, lethargy, and stiffness.
How can you tell if your pain is musculoskeletal?
Pain in the muscles, bones, ligaments, tendons, and nerves is known as Muscle skeletal pain. This discomfort might be felt in only one part of the body, such as your back. If you have a widespread condition, such as fibromyalgia, you may experience it throughout your body.
What causes musculoskeletal pain?
Muscle and skeletal pain can have a variety of causes. The wear and tear of daily activities can cause muscle tissue injuries. Jerking movements, car accidents, falls, fractures, sprains, dislocations, and direct strikes to the muscle can all result in musculoskeletal discomfort.
What are the top 5 symptoms of a musculoskeletal injury?
Swelling, redness, or trouble moving a specific body area are all symptoms. Numbness, tingling, and discomfort are examples of symptoms. symptoms might arise suddenly (as in a single occurrence resulting in an injury) or gradually over time.
How long does it take to recover from muscle pain?
Once the acute inflammation reduces, the bones and soft tissues will settle during the next 6 weeks. The pain will be the worst during the first three weeks, then gradually improve as the bone and soft tissues begin to fuse (the early stage of healing).
Is musculoskeletal discomfort considered a disability?
If your existing musculoskeletal problem causes loss of function, it may be judged serious enough to qualify for disability benefits. Deformity of the joints. Joint annihilation.