Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain (Long-term) characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, tiredness, sleep difficulties, and soreness at specific body spots. According to researchers, Fibro myositis increases painful sensations by altering how your brain and spinal cord receive painful and no painful impulses.
It is more common in women than in men. In addition to temporomandibular joint (TMJ) problems, anxiety, melancholy, and irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia patients frequently get tension headaches.
Who Gets Fibromyalgia?
Fibromyalgia can affect everyone, although women are more likely than males to develop it. It can affect people of any age, including youngsters, but it commonly begins in middle life, and the likelihood of having it grows with age.
If you have other diseases, especially rheumatic diseases, psychological disorders, or pain-causing conditions, you are more likely to have Fibro myositis. These disorders include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Lupus erythematosus (often known as lupus)
- Ankylosing spondylitis is a type of arthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Anxiety or depression
- Back chronic pain
- Irritable bowel syndrome
Fibro myositis runs in families, and some experts believe that specific genes may increase your risk of developing it. However, the condition can occur in people who have no family history of it.
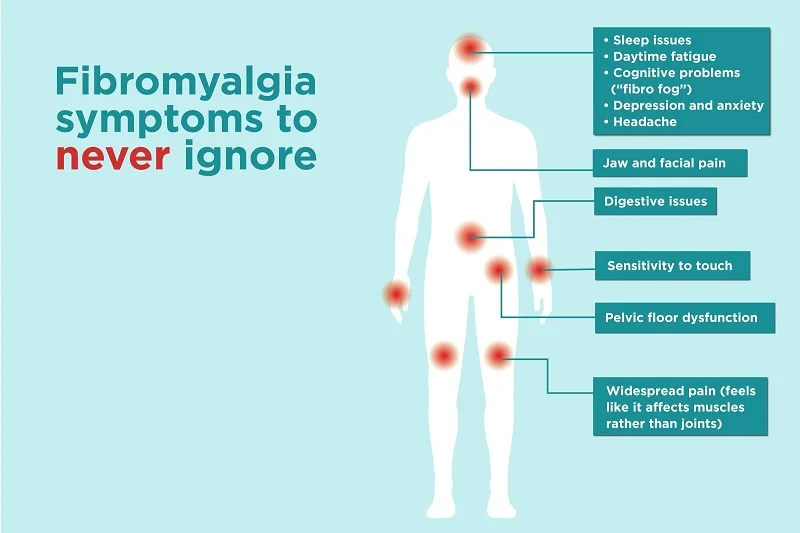
Symptoms
The following are the symptoms of fibromyalgia:
Widespread pain
Fibromyalgia pain is frequently described as a persistent dull aching that has lasted at least three months. To be considered widespread, the discomfort must be felt on all sides of your body, as well as above and below your waist.
Fatigue
People with fibro myositis frequently wake up exhausted, despite resting for significant amounts of time. Pain frequently disrupts sleep, and many Fibro myositis patients have other sleep disorders, such as restless legs syndrome and sleep apnea.
Cognitive difficulties
A symptom known as “fibro fog” hinders the capacity to focus, pay attention, and concentrate on mental tasks.
- Memory loss
- Having problems concentrating
- Difficulty remaining alert
Hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle or pregnancy:
When your hormone levels decline, you may experience greater difficulty sleeping, more widespread pain, or headaches. Your menstrual cycles may also be more painful.
Causes
Many studies believe that fibromyalgia patient’s brains and spinal cords change as a result of frequent nerve stimulation. This alteration entails an abnormal rise in the amounts of specific pain-signaling molecules in the brain.
Many factors are thought to have contributed to these developments, including:
Genetics
Given that fibro myositis frequently runs in families, you may be more prone to acquiring the condition if you have specific genetic abnormalities.
Infections
fibro myositis appears to be caused by or increased by certain diseases.
Physical or emotional events
Sometimes a physical incident, like an automobile collision, might set off Fibro myositis. Extended psychological strain could potentially be the cause of the illness.
Risk factors
Your age: Fibromyalgia is more common in people over the age of 40. It can, however, affect anyone, including children.
Your sex at birth was: People who are allocated female at birth are twice as likely to have Fibro myositis.
Chronic diseases: Fibromyalgia is more common in people who have osteoarthritis, depression, mental problems, persistent back pain, or irritable bowel syndrome.
Traumas: Fibromyalgia can occur in those who have suffered physical or mental stress or a catastrophic injury.
Treatment
Fibromyalgia treatment seeks to alleviate symptoms and enhance quality of life. There is no single treatment that can alleviate all symptoms, and treatments that work for one person may not work for another.
You may need to try several therapies to discover a combination that works for you.

The three primary treatments for fibromyalgia are:
- Exercise
- Talking treatments
- Medicines
Exercise
If you have fibro myositis, you should be physically active. If you’re in pain, this can be challenging, but regular exercise has been found to help reduce discomfort and improve overall quality of life.
Talking treatments
Two talking therapies may be able to assist in lowering fibro myositis pain. They are as follows:
Acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT): where you learn to accept what is beyond your control and commit to making life-changing improvements.
ACT has been demonstrated to improve sleep quality, decrease pain, and aid in the management of negative thoughts and feelings.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT): a talking treatment that can help you manage your challenges by altering your thinking and behavior.
CBT can also help persons with chronic pain improve their quality of life.
Medicine
Some medicines can be prescribed to assist in relieving fibromyalgia. They can also help you sleep better, feel better emotionally, and have a better overall quality of life.
There are some variety of types. The following are commonly used to treat fibromyalgia:
FAQs
Q1) what is life expectancy with fibromyalgia?
Ans: These symptoms vary in severity and appear and disappear over time. There are flare-ups followed by periods with few or no symptoms. However, it is unlikely that they will ever completely vanish. Fibromyalgia, on the other hand, is not fatal and does not affect life expectancy.
Q2) what is the most common age to get Fibro myositis?
Ans: The average age range for Fibro myositis diagnosis is 35 to 45 years old, but most people have experienced symptoms, including chronic pain, from childhood.
Q3) what does fibro myositis pain feel like?
Ans: Some patients have constant stabbing pain throughout their bodies, while others have a continuous, duller ache. A cool breeze or a forceful handshake can produce significant and even excruciating discomfort in those with severe fibro myositis.
Q4) what is the best painkiller for fibromyalgia?
Ans: NSAIDs, opioids, and corticosteroids are not beneficial in the treatment of fibromyalgia pain. The FDA has approved duloxetine (Cymbalta), milnacipran (Savella), and pregabalin (Lyrica) to treat this pain.
Q5) Does fibromyalgia cause weight gain?
Ans: Fibromyalgia (FM) is a phenomenon that affects roughly 3-8% of the general population (1-3). It is characterized largely by persistent pain, and exhaustion, often with significant weight gain, and sleep disturbance.
Q6) what is the number one cause of fibromyalgia?
Ans: One of the main beliefs is that persons with fibromyalgia have altered the way the central nervous system receives pain impulses sent throughout the body. This could be due to changes in the neurological system’s molecules.
Q7) what not to do with Fibro myositis?
Ans: Participating in activities when in pain is likely to result in additional days of suffering. Sugar reduces blood pH levels, aggravating Fibro myositis. Due to candida overgrowth, acidic soft drinks and fruit drinks laden with sugar should be avoided.
Q8) what activities make fibromyalgia worse?
Ans: Fibromyalgia patients should only do modest, everyday workouts. Strenuous activities or over-exercising can aggravate the pain.
Q9) Can I test myself for fibro myositis?
Ans: Consult your doctor if you suspect you have fibro myositis. It is difficult to diagnose because there is no specific test for the disorder. Symptoms can also vary from person to person and are comparable to those of several other diseases.
Q10) can muscle relaxers help fibromyalgia?
Ans: If your muscles are tense, your doctor may prescribe muscle relaxants to relieve the tension. They’ll assist you in regaining range of motion in a frozen shoulder or leg. Muscle relaxants can also help with tiredness, pain, and sleep.